Pathology II Exam III (Mini-Block) Flashcards
The chronic pyogranulomatous pneumonia pictured is fairly characteristic of which bacterial infection in foals?

Rhodococcus equi
What is the etiology for Glasser’s Disease?
Haemophilus parasuis
What is the most likely etiology for verminous bronchitis in sheep and goats?
Dictyocaulus filaria
Adenomas and carcinomas of parathyroid glands often secrete excessive amounts of PTH, resulting in a syndrome of:
primary hyperparathyroidism
The Cerebral Cortical Neuronal Necrosis pictured is likely a result of hypoglycemia resulting from:

Insulin-producing β cell tumor
What is the main pathogen associated with enzootic pneumonia in a pig?

Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
The organism induces a suppurative or cattarhal bronchopneumonia with BALT hyperplasia that is very characteristic.

Atherosclerosis plaques are made up of ________ and __________
Atherosclerosis plaques are made up of cholesterol and lipids
___________ is a generic term applied to the thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls
Arteriosclerosis
What is considered to be the most important pattern of arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the most important pattern of arteriosclerosis and is characterized by the presence of atheromas (of atheromatous plaques) within the intima and media. These plaques contain cholesterol and other lipids

Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumonia is (as the name suggests) a highly contagious and often fatal disease of pig 2-5 months of age.
What is the etiology?

Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae

T/F: Formation of chondroids is a common sequelae to Guttural Pouch Mycosis in horses
False
Chondroid formation is associated with STRANGLES

An old horse presented with epistaxis. This pedunculated tumor-like lesion was found upon post-mortem examination.
What is this called?

Ethmoidal hematoma
The exact etiology is unknown
In dogs, which cells are responsible for removing circulating bacteria and other particles from the blood?
Kupffer cells (liver) and splenic macrophages
This pattern of pneumonia in pigs is very characteristic of infection by which bacterial organism?

Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
The name of the disease is Porcine Contagious Pleuropneumoniae

An increase in dermal mucin resulting in dermal thickening is referred to as:
Myxedema
Regarding thyroid carcinomas, what is the earliest and most frequent site of metastasis?
Lungs
Early in the course of development, thyroid carcinomas invade branches of the thyroid vein
The ‘chondroids’ pictured are associated with which condition in horses?

Strangles
What are the top two etiologies that present with coronary atherosclerosis in dogs?

Diabetes mellitus and Hypothyroidism
Kids (goats) affected with goiter are most likely __________
(hyperthyroid, euthyroid, hypothyroid)
Euthyroid or hypothyroid
The image shows fibrinous rhinitis in a calf with Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR). What is the etiology for IBR?

Bovine herpesvirus 1
Fatal rupture of the uterine artery during parturition occurs occasionally in aged mares with low serum ________ levels
Fatal rupture of the uterine artery during parturition occurs occasionally in aged mares with low serum copper levels
T/F: Healthy bronchioles contain goblet cells
False
Which infectious agent is believed to play a primary role in Canine Infectious Tracheobronchitis (Kennel Cough)?
Bordetella bronchiseptica
CAV-2, CPIV-2, and to a lesser extent Canine Distemper Virus and Mycoplasma spp. have predisposing roles
Guttural pouch mycosis is caused by infection with ________________

Aspergillus fumigatus or other Aspergillus species
T/F: The clinical alterations observed with functional β cell neoplasms are the result of excessive insulin secretion and the development of severe hyperglycemia
False.
The clinical alterations observed with functional β cell neoplasms are the result of excessive insulin secretion and the development of severe hyPOglycemia
What is the name of this condition in pigs?

Atrophic rhinitis
This is a multifactorial disease in growing pigs. It is thought to be the result of a combined infection of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida types D and A
What do we call rhinitis in rabbits as a result of P. multocida?
Snuffles
The world’s most adorable disease name
T/F: β cell degeneration can result in diabetes mellitus
True
Woah, dead rabbit.
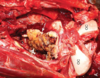
What is the etiological agent for the fibrinosuppurative pleuropneumonia shown in the image?

Pasteurella multocida
The neoplasms most frequently arising in pancreatic islets are adenomas and carcinomas derived from:
β cells