Lecture 9: Culture and Multiracial Families Flashcards
How do we classify different cultures? [6]
- Collectivistic vs. Individualistic (Triandis)
- On the basis of group values, goals, duties
- Interdependent vs. Independent (Markus & Kitayama)
- On the basis of self-construals, identity (more recent categorization)
- Somewhat interchangeable
- What aspects might these groups differ on (e.g. parenting)?
intercultural strategies model [6]
- Developed by John Berry, famous acculturation researcher
- Different strategies for how people moving into a culture + receiving culture will interact with each other depending on the orientation they hold
- Parent-child mismatch + discord in integration strategies
- Usually b/c children adapt better + have more peers in the host culture
- Parents usually have the other three (not integration)

bicultural frame switching [5]
- How one should switch between two lenses/cultural meaning systems competently
- cultural meaning systems: a framework for interpreting and directing affect, cognition, and behavior
- cultural frame-switching: moving between different cultural meaning systems in response to situational cues
- Is frame-switching always good?
- It’s like multitasking; using two frames simultaneously means you might not be doing well in either
3 aspects to bicultural identity [3]
- Can integrate both cultures in everyday life
- Can follow norms of behaviour in both cultures
- Can switch behavior depending on the cultural demands of a situation
Benet-Martinez et al. (2002) [6]
(hint: bicultural identity integration)
- Chinese-American Ps given American vs. Chinese prime
- Completed bicultural identity questionnaire; 8-point Likert Scale
- Rated why one fish was swimming apart from others
- 9-point Likert scale: 1=because fish is influenced by group (e.g. being pressured, teased, or chased by others); 9=because fish is influenced by internal traits (e.g. personal objective or leadership)
- Moderation effect of cultural priming on attributions of fish behaviour
- Low BII → complete rejection of both cultures, opposite results of primed culture

parent-child acculturation discrepancy [4]
- Mismatch between child + parent integration strategies → potentially leads to:
- Family conflict
- Unsupportive parenting
- Prior two can sometimes → negative child outcomes
Kim et al. (2013) [6]
(hint: acculturation discrepancy)
- Acculturation discrepancy + adolescent outcomes
- Chinese-American Ps (parents + adolescents) at two time points (HS)
- Measured acculturation discrepancy (Ps + As); sense of alienation (Ps + As); supportive parenting (warmth, reasoning, monitoring); adolescent adjustment (academic, emotional)
- Only American orientation discrepancy had an impact; no discrepancy was found in Chinese cultural maintenance
- Fathers: depression + lower GPA; mothers: only GPA
- Fathers + mothers talk differently to their children, + maybe differences in value of patriarch for Chinese families
positive outcomes of acculturation [3]
- One possibility: greater responsibility and resilience
- e.g. Through language brokering → being a spokesperson for your family that doesn’t speak the host language very well
- Also having gone through acculturative stress
issues with “cross” cultural [6]
- Greater difference within countries than between them!
- Patricia Greenfield (JCCP, 2014): claims that these within country differences are due to globalization and expansion of (global) commerce
- Media effects as well: internet and facile exposure to other cultures and incorporation of other value systems
- Within a country: both individualist and collectivist systems exist?
- Isolated, rural, poor, subsistence based, home-educated, simple technology → more collectivist based
- Connected to world, urban, rich, commerce-based, heterogenous → more individualist based
parental concerns in multiracial families [8]
- Discussion of racial identity
- Limited knowledge of multiracial identity and related issues
- Ambivalence in acknowledgement; don’t know if they want to address the multiracial identity of their children (when children are younger)
- Experiences of racism due to being in mixed-race relationships
- How do you address this if it happens when you’re with your child?
- Physical appearance; stress of not looking like either of your parents (am I adopted?)
- Pros and cons to integration of ethnicity (and sometimes, culture)
- Curiosity (and worry); often as a result of all prior factors
navigating multiracial parenting [8]
- Multiracial children from 2 monoracial parents → higher risk of mental, physical, and behavior problems
- Usually b/c of society’s inability the role of being multiracial, identity of being multiracial, + challenges faced as a result
- Everyone will want to categorize you as one or the other; difficulties trying to identify as both
- Each parent’s perspective, disagreements; don’t understand unique MR/ME experience
- e.g. double rejection/dual discrimination; not accepted by either race completely
- Parents must modify parenting style and response → flexibility + sensitivity
- Show warmth + support even if you don’t understand what’s happening
- Perceive the issues and properly respond
Crippen & Brew: intercultural parenting strategies [8]
- Mixed-culture couples; identified 2 areas of concern in adapting to differences between cultures
- How are differences perceived?
* Minimized, (Differentiated, Transcended,) Emphasized
* i.e. Differences don’t matter vs. these differences are a huge problem
- How are differences perceived?
- Can there be mutual agreement of differences in order to reach a solution??
* Low (no), asymmetrical (mother or father accommodates), convergent (third culture/space), high (yes)
* i.e. low disagreement on how minority culture status is addressed vs. trying to accommodate
- Can there be mutual agreement of differences in order to reach a solution??
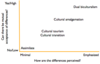
assimilate [1]
(intercultural parenting strategies)
- Unilateral accommodation (usually on part of minority parent)
cultural tourism [2]
(intercultural parenting strategies)
- Lower investment in teaching of cultural values (especially from minority culture)
- Superficially celebrate certain holidays; usually if minority is dad
cultural transition [2]
(intercultural parenting strategies)
- Explicitly teaching the child values from the minority culture
- Usually if minority is mom

